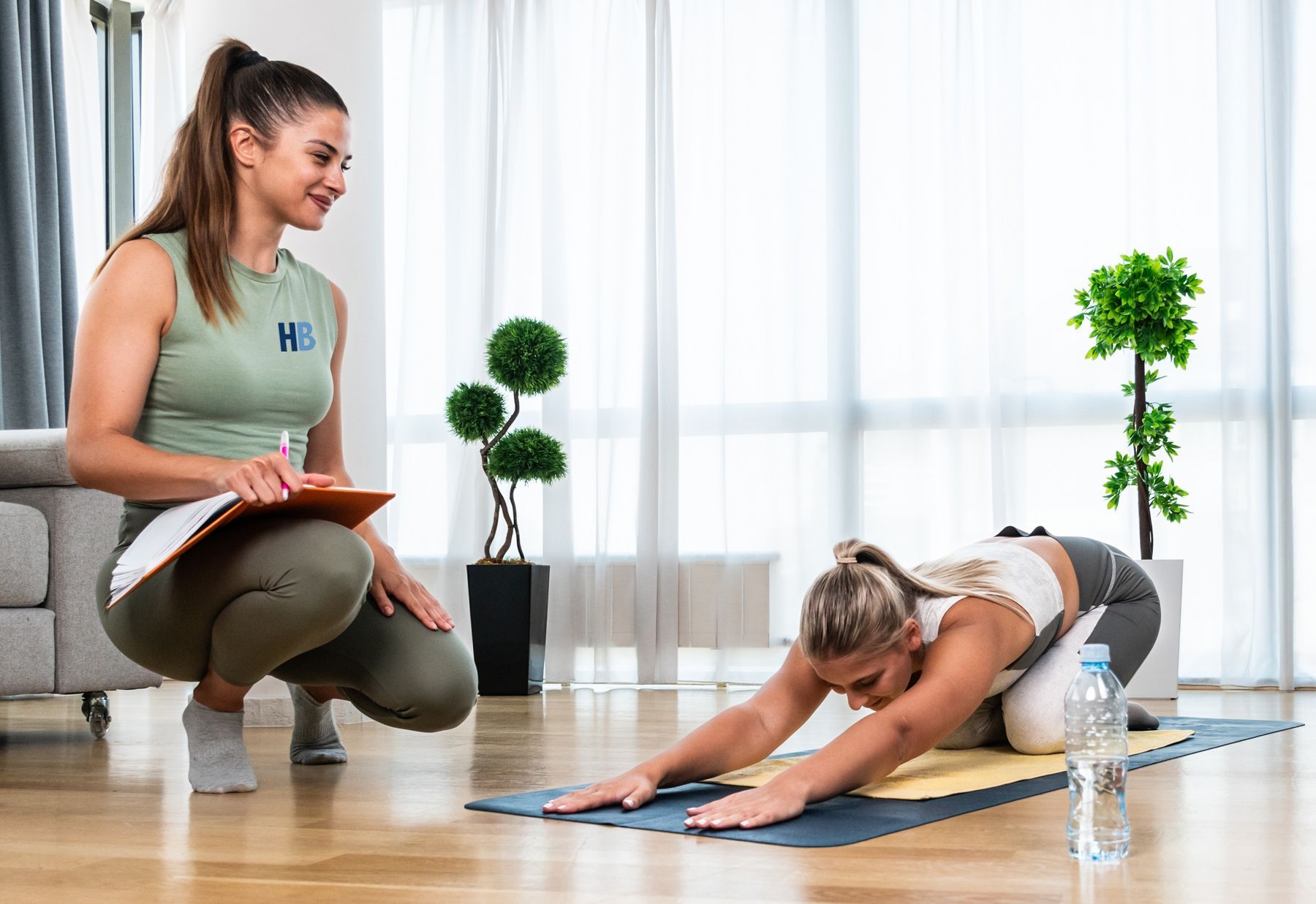
The Importance of Maintaining Flexibility
Flexibility is a vital aspect of physical fitness that encompasses the ability to move joints and muscles through a full range of motion.
Flexibility refers to the capacity of muscles, tendons, and joints to move freely and comfortably through a complete range of motion. It encompasses muscle flexibility, which involves lengthening and stretching muscles, and joint Flexibility, which involves moving joints without discomfort or restrictions.
Flexibility holds significant importance for several reasons. Flexible muscles and joints enable a more comprehensive range of motion, increasing performance potential in various activities and sports. Adequate Flexibility decreases the risk of musculoskeletal injuries by ensuring muscles and tendons can move freely without excessive strain.
Flexibility facilitates everyday movements like bending, reaching, and twisting, making tasks easier and reducing the likelihood of strain or injury. Flexibility exercises promote relaxation, reduce stress levels, improve blood circulation, and enhance overall physical and mental well-being. Learn more by asking your HomeBodies Personal Trainer.
Flexibility plays a crucial role in maintaining the health and functionality of muscles. When muscles are flexible, they can contract and relax effectively, leading to improved muscle performance, reduced muscle tension, and enhanced muscle coordination. Flexibility also helps to prevent the formation of adhesions and scar tissue within the muscles, which can impede their function and lead to pain and stiffness.
Who Benefits Most from Maintaining Flexibility?
While Flexibility is important for everyone, certain individuals benefit the most from incorporating flexibility exercises into their routine. These include:
- Athletes: Flexibility enhances athletic performance by improving agility, balance, and range of motion while reducing the risk of sports-related injuries.
- Older Adults: Aging can lead to a natural decline in Flexibility, making older adults more susceptible to mobility issues and injuries. Regular flexibility exercises help maintain joint mobility, prevent stiffness, and improve overall functional ability.
- Office Workers: Sedentary lifestyles and prolonged sitting can cause muscle imbalances and postural problems. Flexibility exercises help counteract these issues, reducing the risk of chronic pain and musculoskeletal disorders and promoting better posture.
How to Maintain a Flexible Lifestyle
Maintaining Flexibility requires regular practice and dedication. Your HoneBodies personal trainer can review effective strategies that may include:
- Stretching Exercises: Incorporate both dynamic stretches (before physical activity) and static stretches (after exercise) to target major muscle groups and improve Flexibility.
- Yoga or Pilates: Engaging in yoga or Pilates classes enhances Flexibility, strength, balance, and body awareness while promoting relaxation and reducing stress levels.
- Regular Physical Activity: Participating in activities such as swimming, dancing, or martial arts promotes overall Flexibility and helps prevent muscle tightness and stiffness.
Consequences of Inflexibility
Insufficient Flexibility can lead to various consequences, including an overall lack of Flexibility, which restricts joint movement, making simple tasks more challenging and potentially leading to poor posture. Reduced Flexibility makes muscles and tendons more prone to strains, sprains, and tears during physical activities or even routine movements. Inflexibility contributes to muscle imbalances, postural problems, and chronic pain conditions such as lower back pain.
The Role of Food and Flexibility
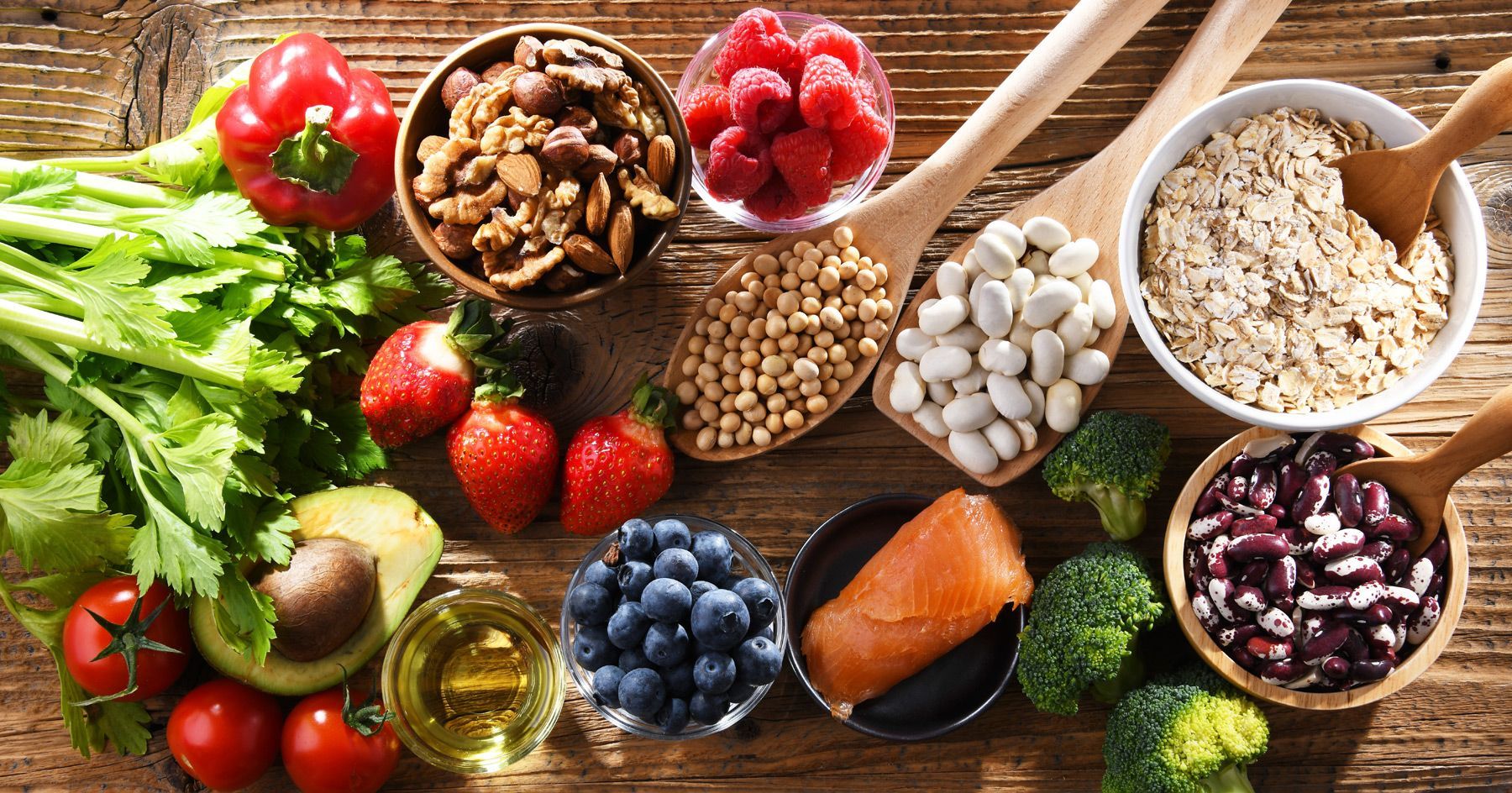
Several foods can help improve flexibility, and others that may hinder it. Here are some dietary changes you can make to become more flexible:
Foods that Can Improve Flexibility
- Fruits and vegetables: Incorporate a variety of colorful fruits and vegetables into your diet, as they are rich in antioxidants and nutrients that help reduce inflammation and improve joint health.
- Omega-3 fatty acids: Include foods like fatty fish (salmon, mackerel, sardines), walnuts, flaxseeds, and chia seeds. Omega-3 fatty acids help reduce inflammation and promote joint flexibility.
- Protein-rich foods: Choose lean proteins like chicken, turkey, fish, tofu, and legumes. Protein helps repair and build muscles, which is essential for flexibility.
- Whole grains: Choose whole grains such as quinoa, brown rice, oats, and whole wheat bread. They provide fiber and nutrients that support muscle and joint health.
- Hydration: Proper hydration is crucial for flexibility. Aim to drink enough water throughout the day to maintain optimal joint lubrication.
Foods that May Hinder Flexibility
- Processed and fried foods tend to be high in unhealthy fats, sugar, and salt, which can cause inflammation and joint stiffness.
- Sugary drinks: Soft drinks, energy drinks, and sugary juices can increase inflammation and hinder flexibility. Instead, drink water or herbal tea.
- Alcohol: Excessive alcohol consumption can lead to dehydration, muscle tightness, and inflammation, negatively affecting flexibility.
- High-sodium foods: Excessive sodium can lead to water retention and joint inflammation, affecting flexibility. Limit your intake of processed foods, canned goods, and fast food.
- Caffeine: While moderate caffeine consumption is generally acceptable, excessive intake can lead to muscle tension and dehydration. Be mindful of caffeine intake from coffee, tea, and energy drinks.
Flexibility plays a vital role in maintaining optimal physical health and overall well-being. By understanding flexibility, recognizing its impact on muscles, identifying the beneficiaries, implementing effective maintenance strategies, and acknowledging the consequences of lacking flexibility, individuals can appreciate the importance of incorporating flexibility exercises into their routines. Being flexible enhances performance, prevents injuries, improves daily functioning, and contributes to a healthier, more enjoyable life.
Try This Post-Yoga Exercise Lunch: Quinoa Buddha Bowl
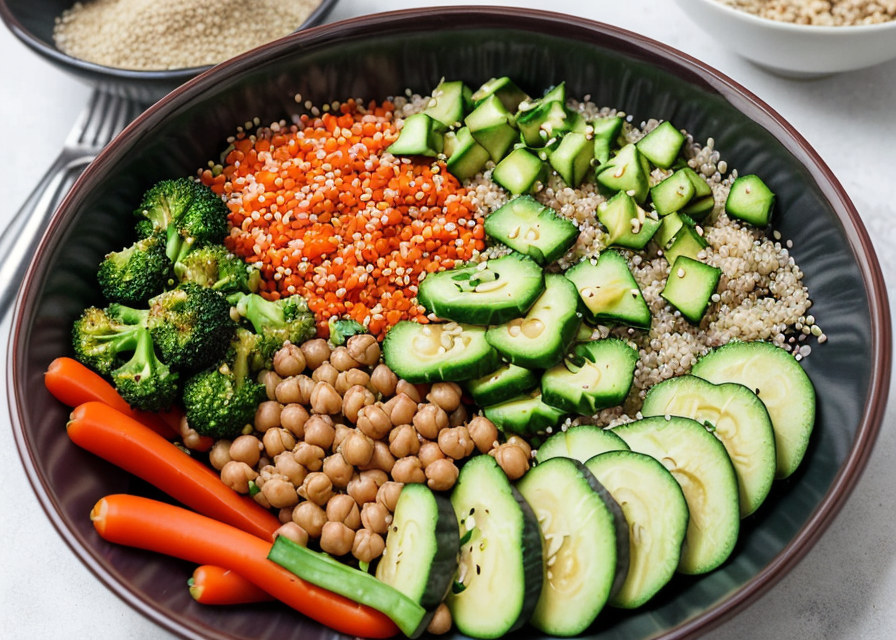

Here's a healthy and nutritious recipe for a post-yoga workout lunch:
- 1 cup cooked quinoa
- 1 cup mixed vegetables (such as broccoli, carrots, bell peppers)
- 1/2 cup chickpeas, drained and rinsed
- 1/4 cup sliced avocado
- 1/4 cup sliced cucumber
- 2 tablespoons chopped fresh cilantro
- 1 tablespoon sesame seeds
- 2 tablespoons lemon juice
- 1 tablespoon olive oil
- Salt and pepper to taste
Instructions:
- Cook quinoa according to package instructions and set aside.
- In a large skillet, heat olive oil over medium heat. Add the mixed vegetables and sauté for 4-5 minutes until tender-crisp.
- Add the cooked chickpeas to the skillet and cook for an additional 2-3 minutes.
- In a small bowl, whisk together lemon juice, olive oil, salt, and pepper to make the dressing.
- In serving bowls, assemble the Buddha bowls by starting with a base of cooked quinoa, then adding the sautéed vegetables and chickpeas.
- Top each bowl with sliced avocado, cucumber, and sprinkle with sesame seeds and chopped cilantro.
- Drizzle the dressing over the bowls and serve.
Enjoy your nourishing and balanced meal after your yoga workout!